What is a Green Schoolyard?
Many schools in Los Angeles are covered in asphalt with little to no shade for students during recess or after school. Schools are often the hottest location in every neighborhood, measuring the same temperature as parking lots and freeways. These treeless, hot environments exacerbate drought, and flooding, and provide no habitat for local and migrating pollinators. What if instead of schools being a drain on our city, they were beneficial?
The solution to making schools a more habitable place to be is to convert outdoor spaces into cool, shady, oases. This can be achieved by replacing asphalt with permeable surfaces where water can soak into the ground, planting trees that provide shade, clean the air, and capture water, and having a diverse selection of plants that provide habitat and food for pollinators.
This illustration visualizes how a green schoolyard can be a living system that provides dynamic learning and play opportunities while creating reciprocal benefits for the school community and the natural world. A green schoolyard should prioritize equity, environmental justice, and climate resilience in school selection and design approaches.
The Multiple Benefits of Green Schoolyards
-
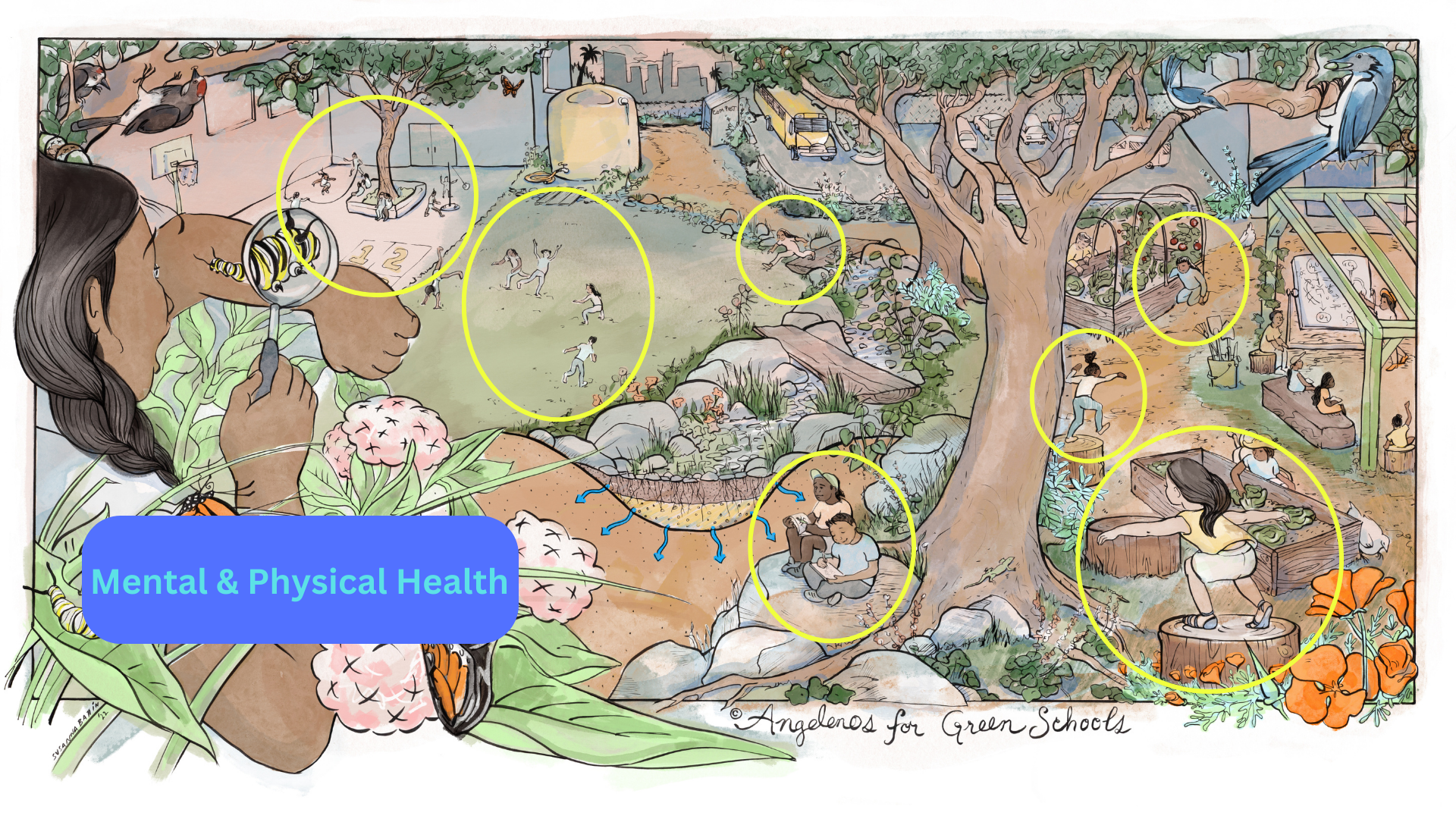
Numerous studies have shown the beneficial connection between the presence of nature and mental health. Trees and plants contribute to a lower heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, and the production of stress hormones (cortisol). Nature also helps to elevate mood and increases the ability to pay attention.
Additionally, trees clean the air and water in neighborhoods with high levels of pollution. This is critical because pollution is the source of above average levels of chronic illness such as heart disease, hypertension, and asthma. Asthma is a leading chronic illness among children and adolescents in the United States as well as one of the leading causes of school absenteeism.Green schoolyards can also improve mental and physical health because they expand the possibilities of how children play during recess and after school. Green infrastructure such as grass, trees, boulders, wood chips, and dry creek beds can lead to more creative and open-ended play opportunities such as gymnastics, chase, hide and seek, and imaginative games with loose parts. Studies show increased physical activity when there is a mix of competitive sport and creative, nature-based play options available.
-
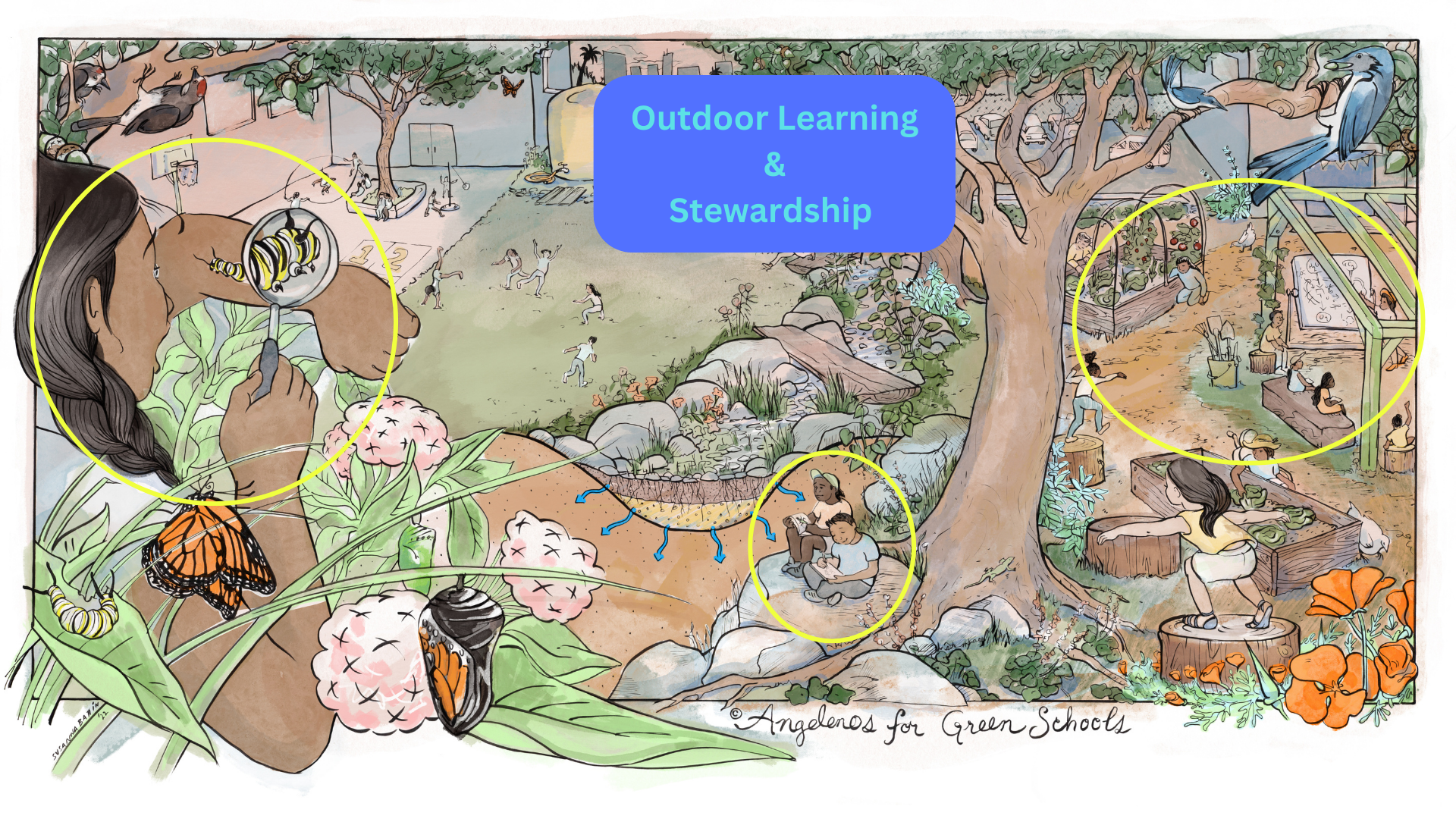
Outdoor learning gives students the opportunity to learn and care for their local natural environment by seeing first hand how human actions positively or negatively impact their surroundings.
Teachers who hold class outside using a nature-based curriculum report that students demonstrate an increased ability to think creatively and problem-solve, and approach their learning more enthusiastically.
Stewardship is the missing link between learning about the challenges our society faces and gaining the skills to do something about it. The act of caring for plants and seeing the relationships they have with water and wildlife help students develop a deeper relationship to their local environment. We have a lot to learn from our Indigenous contemporaries whose ancestors managed this land for 10,000 years, guided by a reciprocal relationship that considered humans as one in the same as the natural world.
-
LAUSD is projected to lose 30% of its students over the next decade and faces a chronic teacher shortage and teacher retention problem. Studies suggest that educators who have the opportunity to take students outdoors to learn are less likely to burn out and enjoy higher job satisfaction. (Paddle and Gilliland, 2016) READ MORE
A cost benefit study conducted by the Trust for Public Land shows that daily attendance and enrollment increases when a school is greened.
-
BIG PICTURE
More green schoolyards mean less asphalt, more trees, and more stormwater captured. LAUSD is the largest landowner in LA County; imagine how much this can help with air quality and urban cooling.
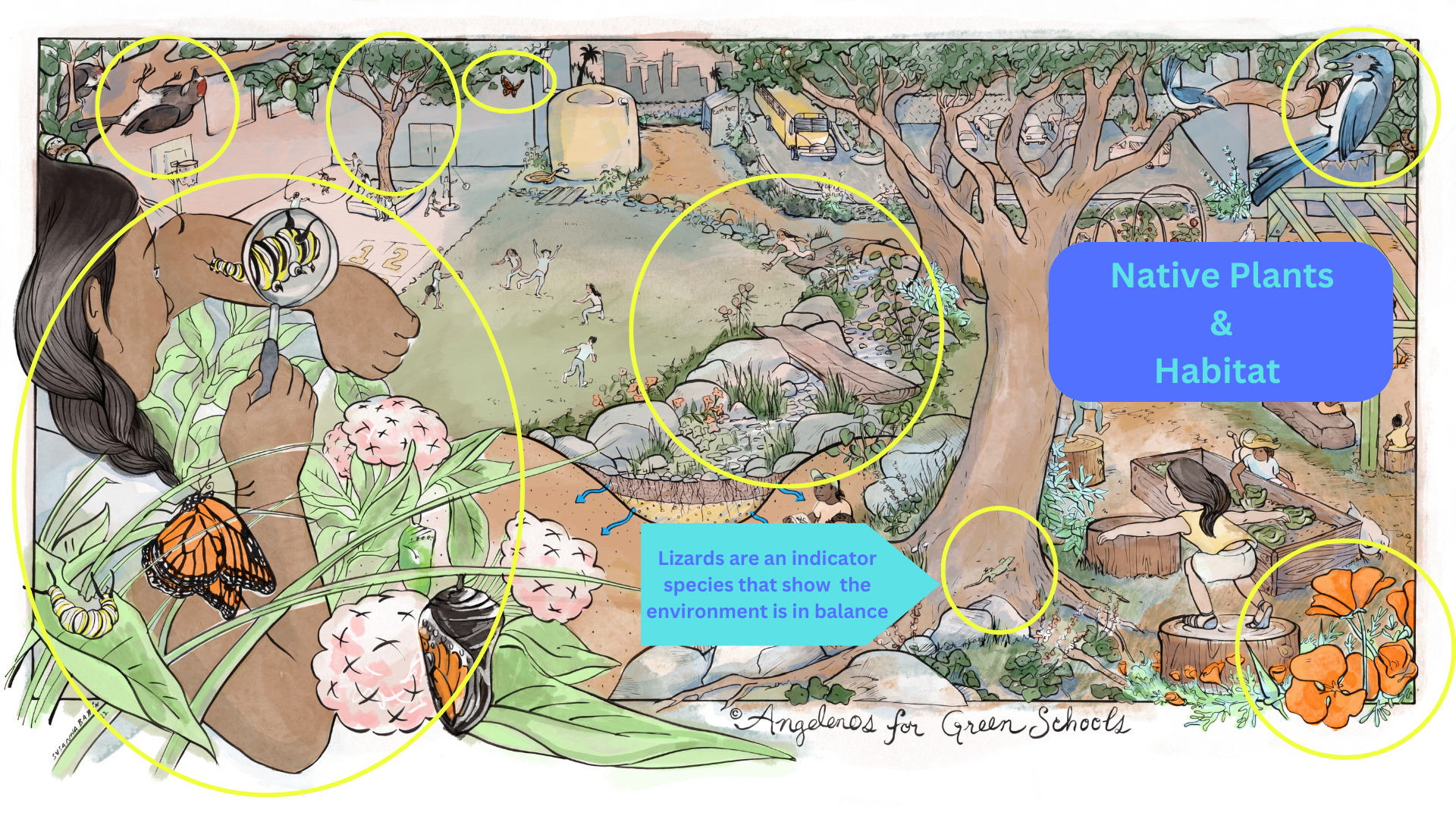
NATIVE HABITAT
Green schools provide essential food, water, shelter, and space for local and migrating wildlife like songbirds, butterflies, and other pollinators. Los Angeles is a critical destination for species migrating between South America to Canada. READ MORESTORMWATER MANAGEMENT
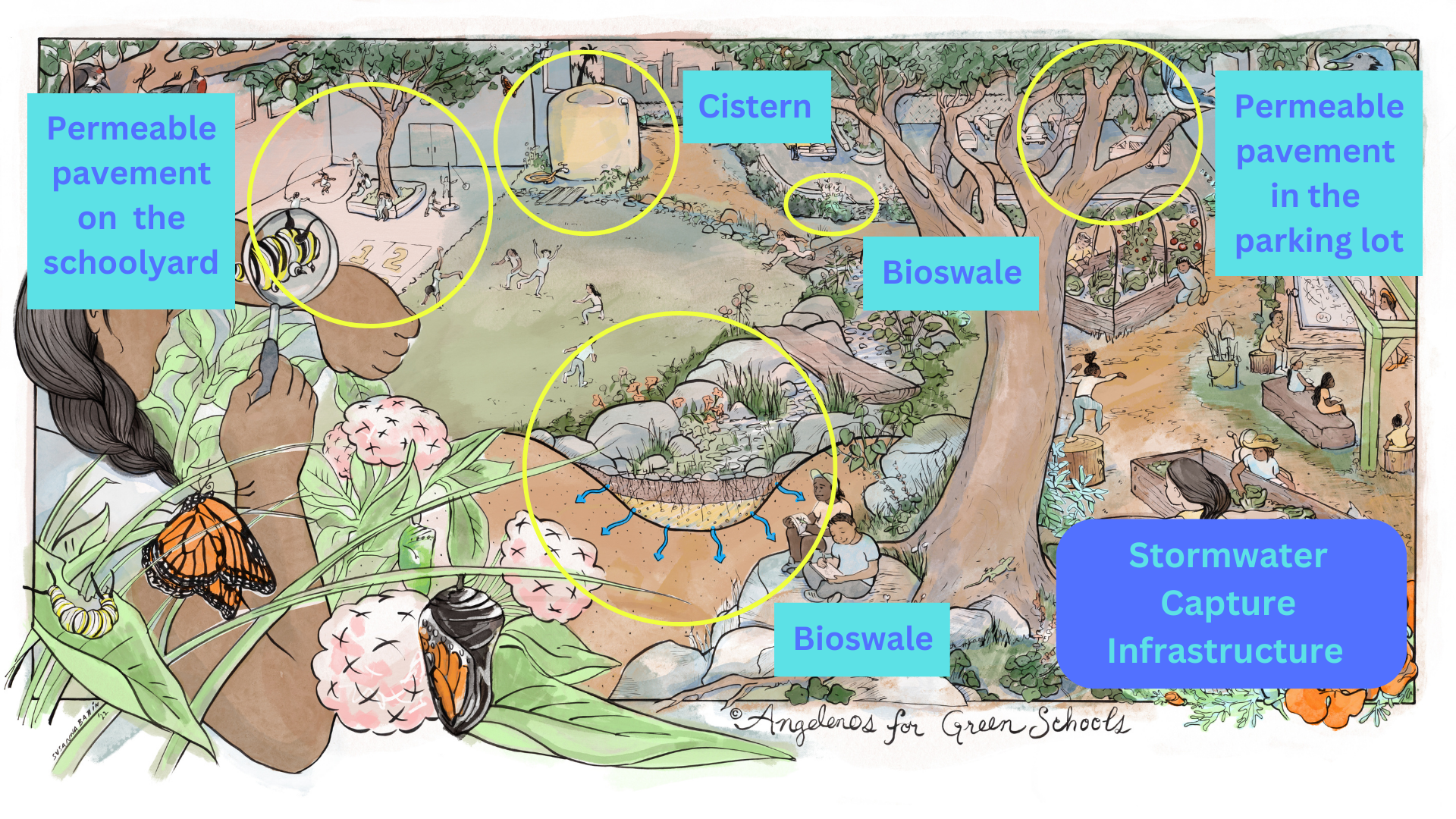
Los Angeles regularly experiences drought conditions but there are ways to be more prepared for these dry spells. By installing infrastructure such as cisterns, bioswales, and permeable pavement, stormwater can be cleaned and captured instead of rushing out to the ocean, full of pollutants. This keeps our waterways cleaner and healthier while recharging groundwater reserves we’ll need in the future. READ MORE
REDUCE HEAT
Schoolyards are often the hottest location in every neighborhood because they are covered in heat absorbing surfaces such as asphalt, concrete, and rubber. When asphalt is removed and replaced with trees, temperatures can be reduced by 9 degrees, making the schoolyard an area that helps to cool down a neighborhood instead of heating it up. READ MORE
Resources
California Green Schoolyards A Cost-benefit Study, Trust for Public Land, 2022
Green Schoolyard District Design Guidelines, Children and Nature Network, 2022
Recess Behaviors of Urban Children 16 Months After a Green Schoolyard Renovation, Human Kinetics Journals, 2021
San Francisco Nature Exploration Area Playbook Design Guide, 2021
Greening schoolyards - An urban resilience perspective, 2020
Physical Activity and Social Behaviors of Urban Children in Green Playgrounds, American Journal of Preventative Medicine, February 2019
California Department of Education Guide to School Site Analysis and Development, 2000